Deploying an instance zone advanced-routing
de:Bereitstellen von einer Instanz Zone erweiterte-routing
nl:Een exemplaar zone geavanceerde-routering implementeren
it:Distribuzione di un'istanza zona-routing avanzato
pt:Implantando uma instância zona avançada-roteamento
es:Implementación de una instancia zona avanzada de enrutamiento
fr:Deploiement d'une instance en zone advanced-routing
This article has been created by an automatic translation software. You can view the article source here.
3. Deploying an instance zone Advance-Routing
Log on to the web interface Cloud public to Ikoula : https://cloudstack.ikoula.com/client/ and go to the 'Bodies' tab and click on the button "add an instance."
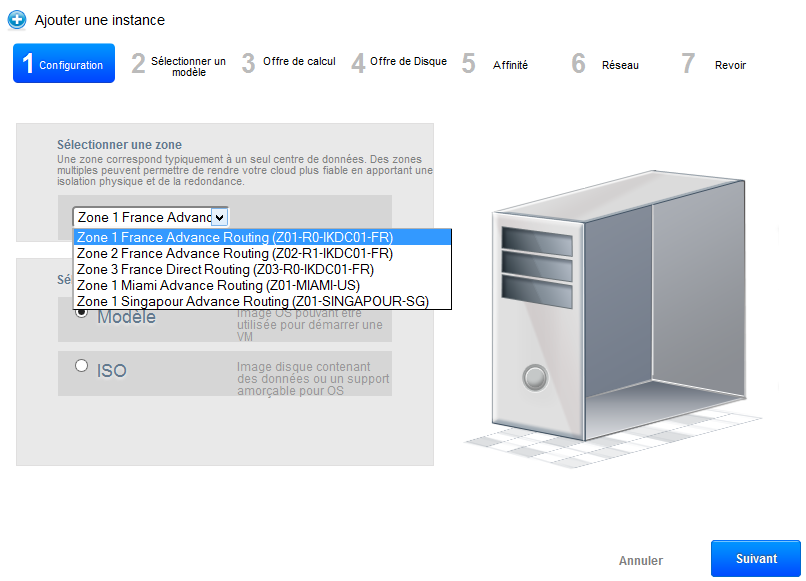
The first step allows yor to choose the one hosting your instance Zone (five areas are currently available ) and a model (preinstalled system /preconfigured ) or an ISO.
For this example we will use a model. Select the image « CentOS 7 – Minimal – 64bits » and click on «next».
The next step is to select the instance configuration, descriptions of the various offers are shown.
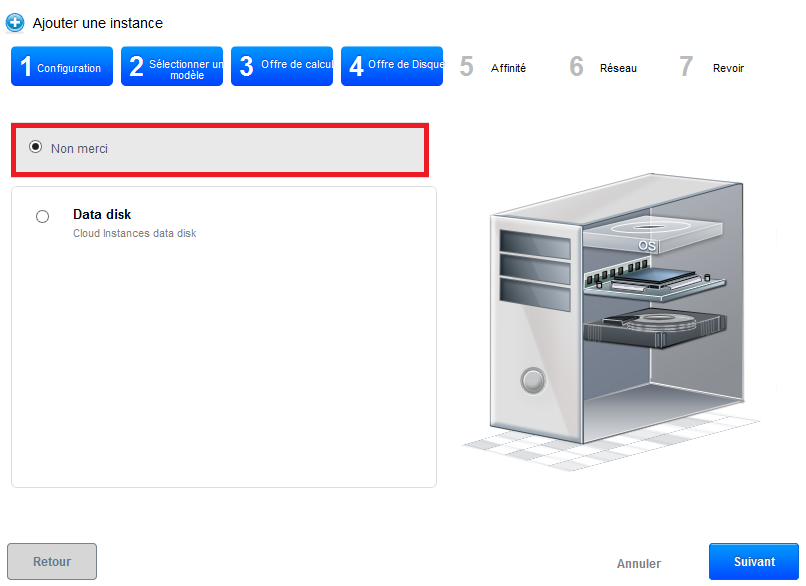
In the next step, we can indicate if we want a DATADISK (data disc ) and its size. We do not want immediate : then click on the button "next".
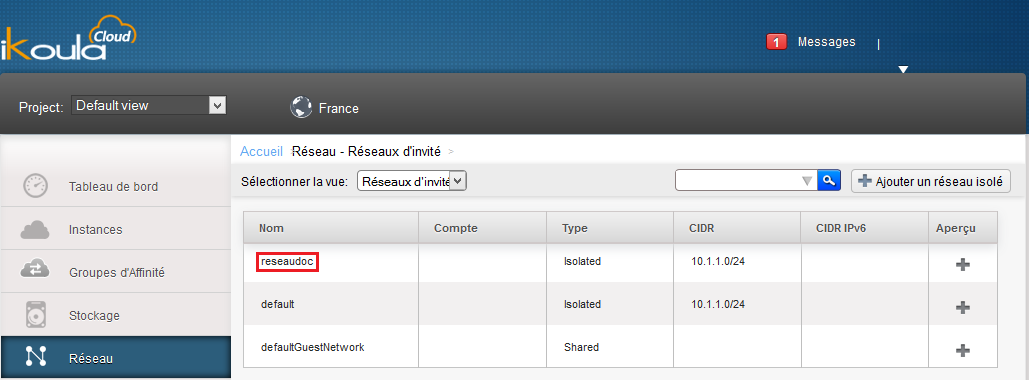
Then there is the selection of the network, if yor already have one or more networks in this area they will appear at the top ("default" in the image below ).
Otherwise, various offers are available for creating (Depending on the service purchased ) in the lower part : 10/100/200/500/1000
Once your choice is made, click on «Next» :
This page allows yor to define a name and /or a group for your instance, these two parameters are optional and only present to help organize you. Once complete, yor can initiate the creation.
The interface is asynchronous, it "makes yor hand" during the deployment of your trial. Yor can see the current actions, in error or terminated in the 'Message' window at the top in the middle of your interface :
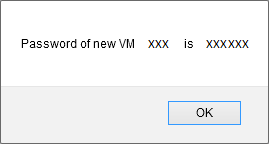
Once the deployment is completed, a pop-up will notify yor of the password of your new instance :
In addition, another, at the bottom of the screen will inform yor of the end of the deployment :
- Examples of network configuration for the instances
Once your instance is created, yor can access it via the KVM available in the window of details of the latter or, for example, to open its port of SSH access (GNU /Linux ) or TerminalServer /RDP (Windows).
- Accessibility outside for an instance type GNU SSH /Linux .
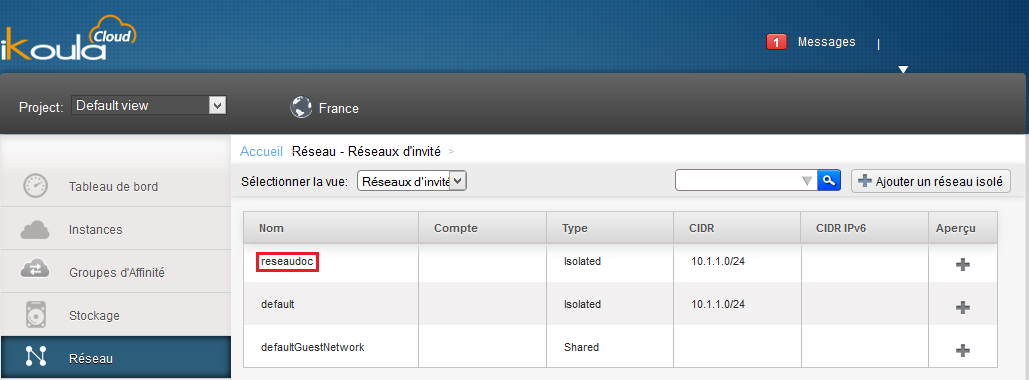
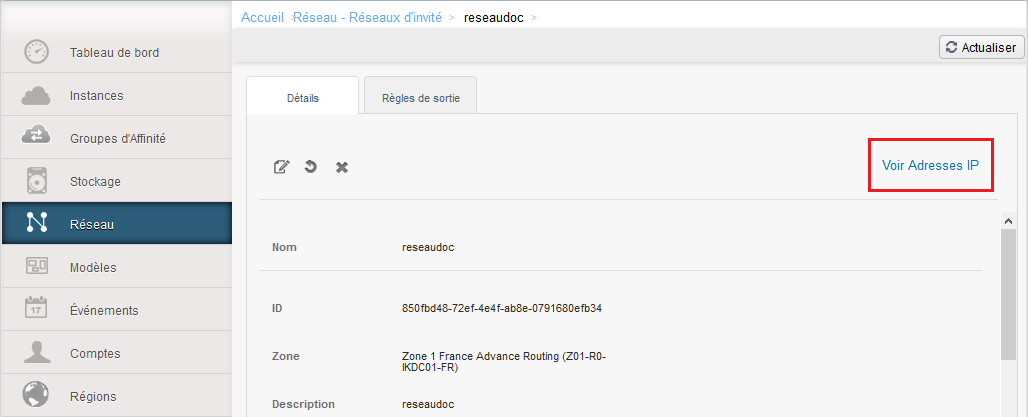
Go to your "Network" tab and click on the name of your network :
Then click on 'See IP addresses' :
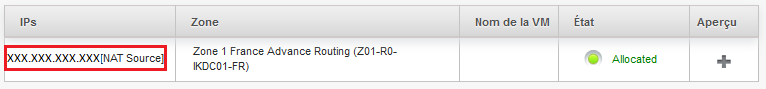
Yor will find the public IP addresses assigned to you, click the one that yor want to configure :
Once on the detail of your public address, click on "Configuration" :
We open the port 22 (SSH ) on your private virtual router, then click on "See all" in the "Firewall" framework :
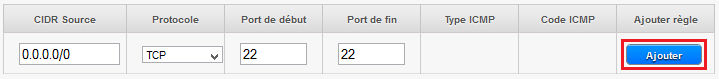
In this screen yor can add the IP address or the network (CIDR notation, e.g. x.x.x.x /24 or 0.0.0.0/0 for everyone ) yor want to allow to connect to TCP port 22 from the outside (i.e. "Internet" ) :
When done, click 'Add' and return to the previous step for, this time, click 'See all' in the setting "Port forwarding" :
In the same way, yor will specify a port (or un intervalle de ports) external (your public IP address ) to match to a port (or un intervalle de ports) internal (on your instance in addressing private ).
In our example, we have created our Firewall rule on port 22, to indicate public port will be port 22 as for the port private (pour une instance où le serveur SSH écoute sur le port par défaut).
After which, you can access your instance en SSH Since the port 22 your public IP.
In this way, it is possible to have multiple instances to listen on the private port 22 and access it from different public ports from outside. If yor only have an instance, specify 22 in public and private port as in our example to access from the port 22 from the outside.
- Accessibility TS /RDP from the outside to an instance type MS Windows.
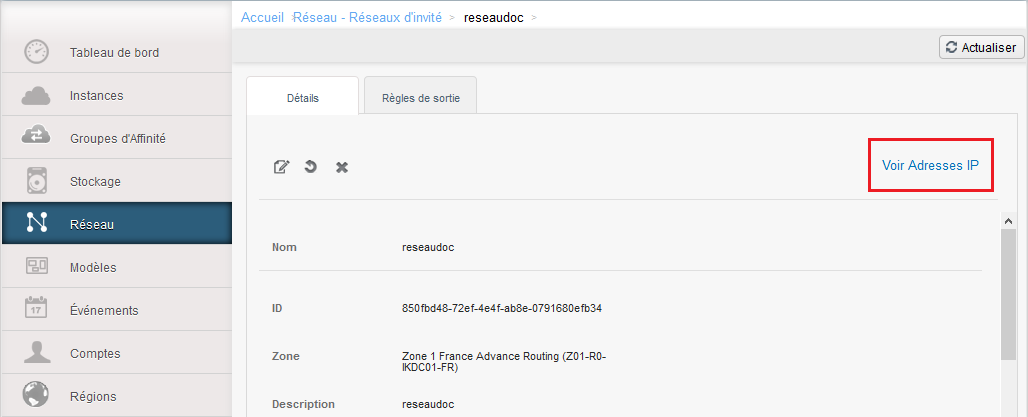
Go to your "Network" tab and click on the name of your network :
Then click on 'See IP addresses' :
Yor will find the public IP addresses assigned to you, click the one that yor want to configure :
Once on the detail of your public address, click on "Configuration" :
We open the port 22 (SSH ) on your private virtual router, then click on "See all" in the "Firewall" framework :
Dans cet écran vous allez pouvoir ajouter l’adresse IP or réseau (CIDR notation, e.g. x.x.x.x /24 or 0.0.0.0/0 for everyone ) yor want to allow to connect to TCP port 3389 from the outside (i.e. "Internet" ) :
When done, click 'Add' and return to the previous step for, this time, click 'See all' in the setting "Port forwarding" :
In the same way, yor will specify a port (or un intervalle de ports) external (your public IP address ) to match to a port (or un intervalle de ports) internal (on your instance in addressing private ).
In our example, we have created our Firewall rule on port 3389, to indicate public port will be port 3389 as for the port private (pour une instance où le serveur SSH écoute sur le port par défaut).
After which, you can access your instance en Terminal Server Since the port 3389 Since your public IP.
In this way, it is possible to have multiple instances to listen on the private port 3389 et y accéder depuis des ports publics différents from the outside or si vous n’avez qu’une instance, indiquez 3389 en port privé et public comme dans notre exemple et y accéder Since the port 3389 from the outside.
See also :
Authorization PING (ICMP /Echo ) from the outside to its public IP
Allow outbound to the outside network flow
This article seemed you to be useful ?
[[Category:[First_steps_on_cloud_public_ikoula]]
















Enable comment auto-refresher