Difference between revisions of "Create an instance RancherOS"
(Created page with "<br /> This article has been created by an automatic translation software. You can view the article source here.<br /><span data-translat...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <span data-link_translate_fr_title="Creer une instance RancherOS" data-link_translate_fr_url="Creer_une_instance_RancherOS"></span>[[:fr:Creer une instance RancherOS]][[fr:Creer une instance RancherOS]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 7 December 2015
fr:Creer une instance RancherOS
This article has been created by an automatic translation software. You can view the article source here.
The procedure below describes how to create an instance RancherOS Cloud Ikoula. RancherOS is the GNU distribution /Linux which is the more minimalist and simple to use Docker. In RancherOS everything is container (including udev and rsyslog e.g. ), Docker is also running as PID process 1 This system (usually init or systemd ). It is also a system that has the advantage of having the latest version of Docker or nearly so interesting when you want to have the latest features of Docker.
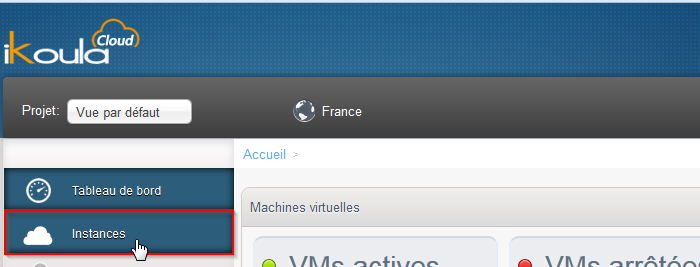
In a first step, connect to the management interface Cloud Ikoula :
Create a new instance :
- Click on 'Bodies' in the vertical left menu :
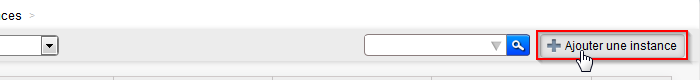
- Click on the button 'Add an instance' :
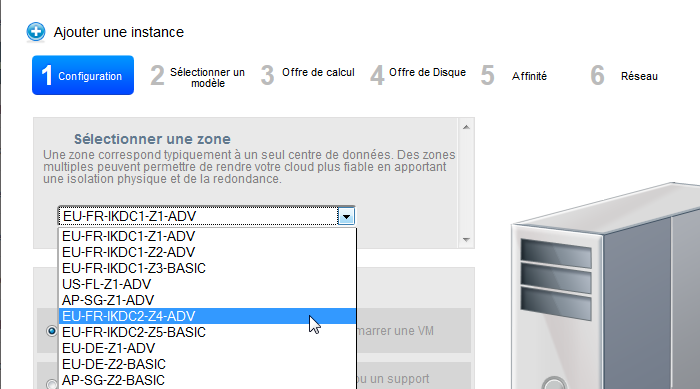
- Select a deployment from the drop-down list box (in our ex ample we will choose a zone advanced networked / name of area ending with "ADV" ) :
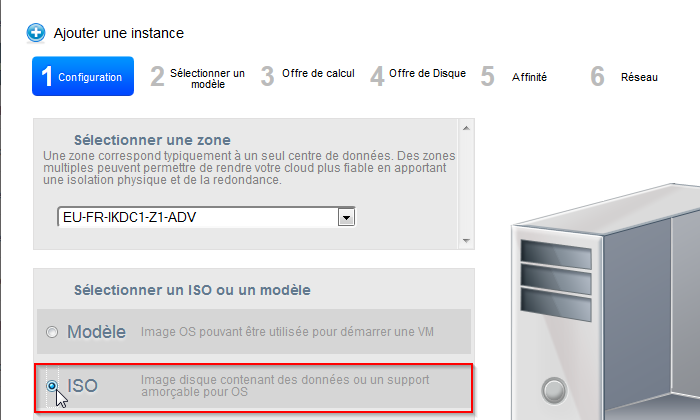
- Select "ISO" :
- Click on «next»
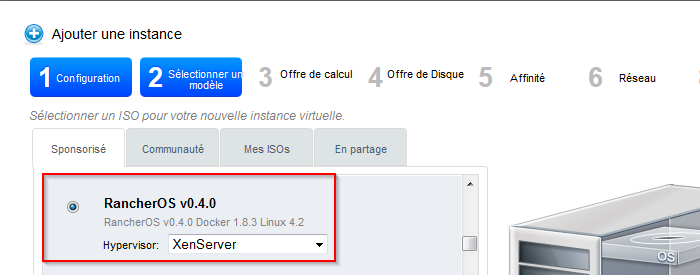
- Select the ISO "RancherOS v 0.4 '. "in the list of the ISO of the sponsored tab :
- Click on «Next»
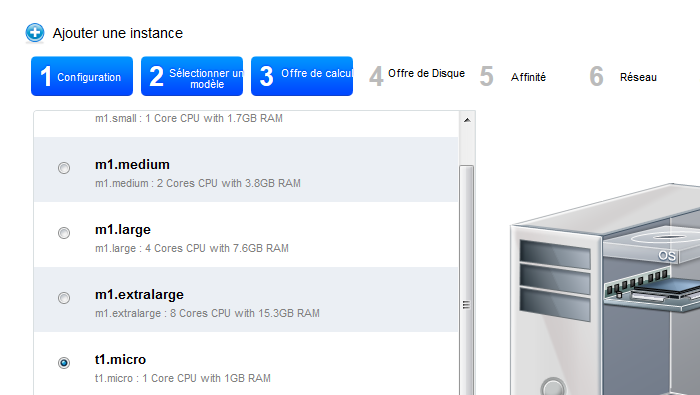
- Choose an offer of calculation :
- Click on «Next»
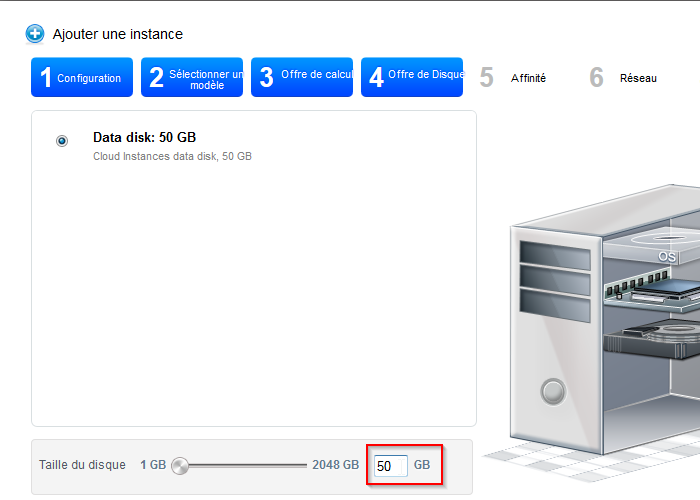
- Enter the size that you want to assign to the virtual disk (rootdisk ) your instance :
- Click "next" twice
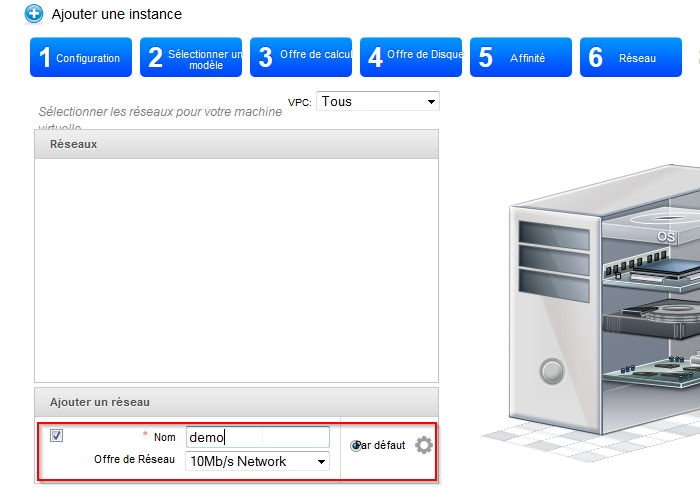
- Add a network by typing a name and the desired network offer or select one of your existing networks :
- Click on "Following"
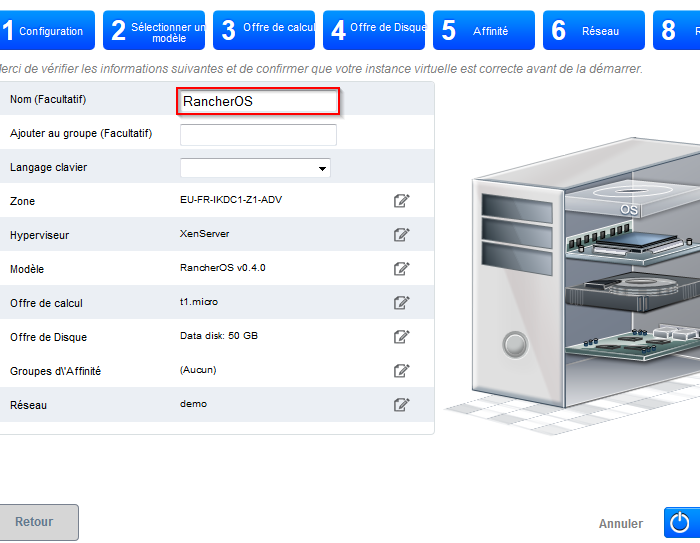
- Define a name for your instance and then click on the button "Start VM" :
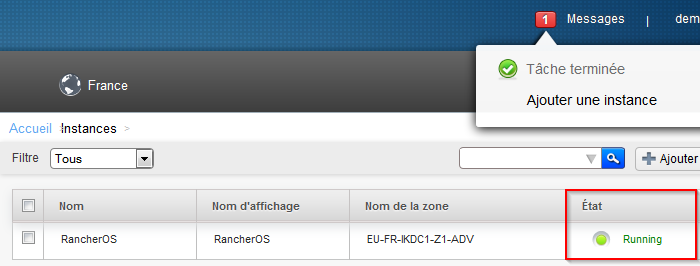
- Wait until your instance is 'running' :
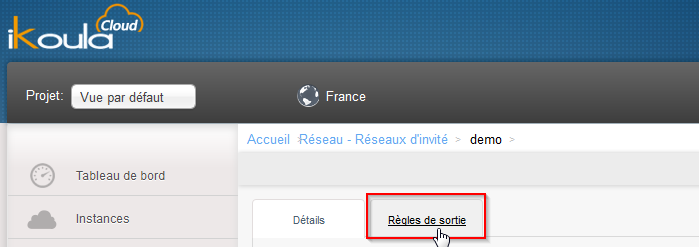
- Click on 'Network' in the left menu vertical on the network of your instance name, and then click 'Exit rules' :
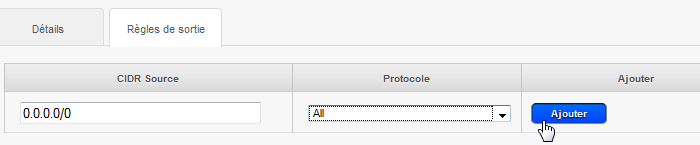
- Add output rule (Firewall ) authorizing the outflow for all protocols :
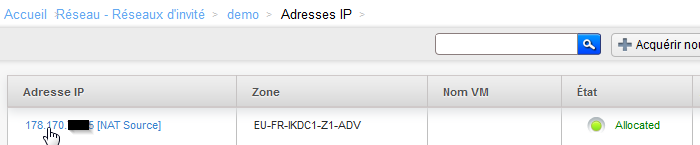
- Go back to the tab "Details" of your network and click on 'See IP addresses' the IP NAT Source, your network address :
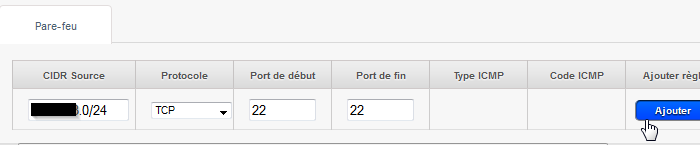
- Click on the tab " '. Configuration' then click 'See all' of firewall and add an inbound firewall rule allowing SSH connections (port 22/TCP ) to your network
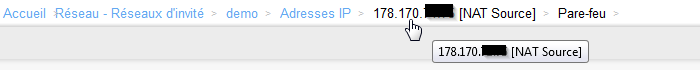
- Re-click on the Source ip address NAT of your network :
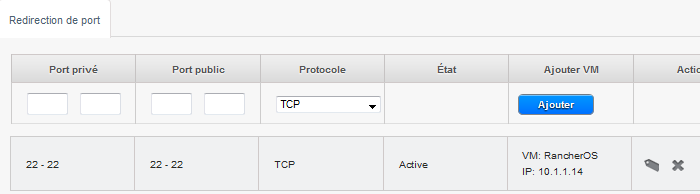
- Click on the button "See all" port forwarding then add a port forwarding rule allowing you to log into SSH on your instance (ex : Private port 22 public port 22 Protocol TCP ) and add your instance and make 'Apply'
- Log into ssh on iso attached to your instance with the "rancher" login and password "rancher" :
demo@pc-demo:~$ ssh rancher@178.170.XX.XX
The authenticity of host '178.170.XX.XX (178.170.XX.XX)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is xx:85:xx:02:xx:bf:xx:b4:xx:1d:xx:1a:xx:3a:xx:0b.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '178.170.XX.XX' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
rancher@178.170.XX.XX's password:
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
- Create a file cloud-config.yml with client public SSH RSA of your workstation key. It is this key that will allow you to connect with the "rancher" ssh login to your instance RancherOS (see http://docs.rancher.com/os/cloud-config/) :
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$ cat << EOF > cloud-config.yml
> #cloud-config
> ssh_authorized_keys:
> - ssh-rsa AAAAB...XXXXXX...YYYY.....ZZZZdemo@pc-demo
> EOF
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
Replace "AAAAB...XXXXXX...YYYY.....ZZZZdemo@pc-demo" by the key SSH rsa public your client workstation in the example above.
- Once the file cloud-config.yml created, run the command " '. sudo install - c ros cloud-config.yml - d /dev/xvda » to install RancherOS on the virtual disk (rootdisk) your instance :
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$ sudo ros install -c cloud-config.yml -d /dev/xvda
INFO[0000] No install type specified...defaulting to generic
Installing from rancher/os:v0.4.1
Continue [y/N]: y
Unable to find image 'rancher/os:v0.4.1' locally
v0.4.1: Pulling from rancher/os
26b82ec3311d: Pull complete
f05335696a9b: Pull complete
8e8fa9d5f794: Pull complete
6cbde7cc282e: Pull complete
ed08d2a1b7fe: Pull complete
3b09e65b0985: Pull complete
87bbc662b44c: Pull complete
f17c535a2c45: Pull complete
f5261f101133: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:320addc8d74521965956b8ec97c025b3d79db2f1e1a83235b767fe0953ef5b88
Status: Downloaded newer image for rancher/os:v0.4.1
+ DEVICE=/dev/xvda
+ [[:fr: -z /dev/xvda ]]
++ wc -l
+++ cut -d / -f3
+++ echo /dev/xvda
++ grep xvda /proc/partitions
+ PARTITION_COUNT=1
+ '[' 1 -gt 1 ']'
+ dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/xvda bs=512 count=2048
2048+0 records in
2048+0 records out
1048576 bytes (1.0 MB) copied, 0.0372273 s, 28.2 MB/s
+ partprobe /dev/xvda
+ fdisk /dev/xvda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.25.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x5ab88c99.
Command (m for help): Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): Partition number (1-4, default 1): First sector (2048-104857599, default 2048): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-104857599, default 104857599):
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 50 GiB.
Command (m for help): The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
++ dirname /scripts/lay-down-os
+ . /scripts/build.conf
++ IMAGE_NAME=rancher/os
++ VERSION=v0.4.1
++ DOCKER_BINARY_URL=https://github.com/rancher/docker/releases/download/v1.9.1-rc1-ros1/docker-1.9.1-rc1
++ COMPILED_KERNEL_URL=https://github.com/rancher/os-kernel/releases/download/Ubuntu-4.2.0-16.19/linux-4.2.3-rancher-x86.tar.gz
++ DFS_IMAGE=rancher/docker:1.9.1-rc1
+ VERSION=v0.4.1
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ case ${OPTION} in
+ DEVICE=/dev/xvda
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ case ${OPTION} in
+ ENV=generic
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ case ${OPTION} in
+ CLOUD_CONFIG=/opt/user_config.yml
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ DIST=/dist
+ CLOUD_CONFIG=/opt/user_config.yml
+ CONSOLE=tty0
+ BASE_DIR=/mnt/new_img
+ PARTITION=/dev/xvda1
+ KERNEL_ARGS=
+ '[' -n generic ']'
+ case ${ENV} in
+ format_and_mount
+ format_device
+ device_defined /dev/xvda
+ [[ -z /dev/xvda ]]
+ mkfs.ext4 -F -i 4096 -L RANCHER_STATE /dev/xvda1
mke2fs 1.42.12 (29-Aug-2014)
Creating filesystem with 13106944 4k blocks and 13107200 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 704a1b35-b886-430e-be0c-fac8e3ca5237
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
+ mount_device
+ local label=RANCHER_STATE
+ local raw=false
+ mkdir -p /mnt/new_img
++ wc -l
++ grep RANCHER_BOOT
++ lsblk -o name
+ '[' 0 -eq 1 ']'
+ local 'mount_opts=-L RANCHER_STATE'
+ '[' false == true ']'
+ mount -L RANCHER_STATE /mnt/new_img
+ trap 'umount /mnt/new_img' EXIT
+ create_boot_dirs
+ mkdir -p /mnt/new_img/boot/grub
+ install_grub
+ grub-install --boot-directory=/mnt/new_img/boot /dev/xvda
Installing for i386-pc platform.
Installation finished. No error reported.
+ /scripts/seed-data /mnt/new_img /opt/user_config.yml
+ BASE_DIR=/mnt/new_img
+ CLOUD_DATA=/opt/user_config.yml
+ IFS=,
+ read -ra FILES
+ '[' -z /mnt/new_img ']'
+ mkdir -p /mnt/new_img/var/lib/rancher/conf/cloud-config.d
+ '[' /opt/user_config.yml '!=' /scripts/conf/empty.yml ']'
+ cp /opt/user_config.yml /mnt/new_img/var/lib/rancher/conf/cloud-config.d/
+ grub2_config ''
+ local grub_cfg=/mnt/new_img/boot/grub/grub.cfg
+ local append_line=
+ cat
+ '[' '!' -z ']'
+ pvgrub_config ''
+ local grub_file=/mnt/new_img/boot/grub/menu.lst
+ local append_line=
+ cat
+ '[' '!' -z ']'
+ install_rancher
+ cp /dist/initrd /mnt/new_img/boot/initrd-v0.4.1-rancheros
+ cp /dist/vmlinuz /mnt/new_img/boot/vmlinuz-v0.4.1-rancheros
+ umount /mnt/new_img
Continue with reboot [y/N]: y
INFO[0103] Rebooting
- Stop your instance and detach the ISO it :
- Start your instance once the ISO detached from this
- Connect to your instance RancherOS in ssh with login 'rancher' from the machine that has the public SSH key that you added to the file cloud-config.yml above :
demo@pc-demo:~$ ssh rancher@178.170.XX.XX
The authenticity of host 178.170.XX.XX (178.170.XX.XX)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is xx:66:xx:c5:xx:bf:xx:b4:xx:47:xx:1a:xx:b8:xx:cf.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '178.170.XX.XX' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
- Your instance has now RancherOS disk :
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$ docker info
Containers: 0
Images: 0
Server Version: 1.9.1-rc1
Storage Driver: overlay
Backing Filesystem: extfs
Execution Driver: native-0.2
Logging Driver: json-file
Kernel Version: 4.2.3-rancher
Operating System: RancherOS (containerized)
CPUs: 1
Total Memory: 990.8 MiB
Name: RancherOS.CloudInstances
ID: CWVI:BCAE:3DPO:2TCG:JKHM:RFVS:47G2:LZOH:4GB3:SP2Z:4A66:AVF7
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
[root@RancherOS rancher]# df -hT
Filesystem Type Size Used Available Use% Mounted on
overlay overlay 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /
tmpfs tmpfs 482.0M 0 482.0M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 495.4M 0 495.4M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /home
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /opt
none tmpfs 495.4M 272.0K 495.1M 0% /run
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/iptables
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/poweroff
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /lib/modules
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/halt
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/shutdown
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/docker
none tmpfs 495.4M 272.0K 495.1M 0% /var/run
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/rkt
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/reboot
devtmpfs devtmpfs 482.0M 0 482.0M 0% /host/dev
shm tmpfs 64.0M 0 64.0M 0% /host/dev/shm
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /lib/firmware
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/log
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/ros
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/rancher
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/system-docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/wait-for-docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/netconf
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/user-docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/rancherctl
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/dockerlaunch
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/respawn
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/rkt
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/wait-for-network
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/docker.dist
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/cloud-init
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/share/ros/os-config.yml
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/rancher/conf
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt.rancher
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/resolv.conf
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/hostname
shm tmpfs 64.0M 0 64.0M 0% /dev/shm
devtmpfs devtmpfs 482.0M 0 482.0M 0% /dev
shm tmpfs 64.0M 0 64.0M 0% /dev/shm
[root@RancherOS rancher]#
You can if you want to make a template of your instance from its rootdisk to deploy others RancherOS (ex: cluster RancherOS /Docker)
Enable comment auto-refresher