Diagnosing a network problem
fr:Diagnostiquer un problème réseau en:Diagnosing a network problem
Introduction
In this article, you will see how to perform a network diagnostic and tools to check the status of the machine.
Ping
The ping is a command to test and verify the accessibility of a machine through the network. It is necessary to launch this command ping followed by the IP or the desired domain as follows.
Linux
On Linux, you will have to open the terminal and launch the following command by replacing the IP or the domain by the desired one:
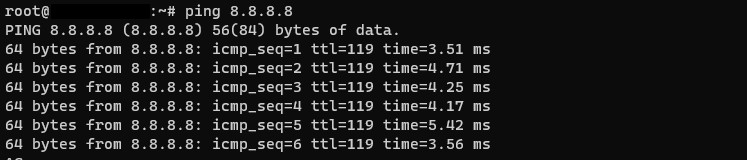
ping 8.8.8.8
This will give us the following overview:
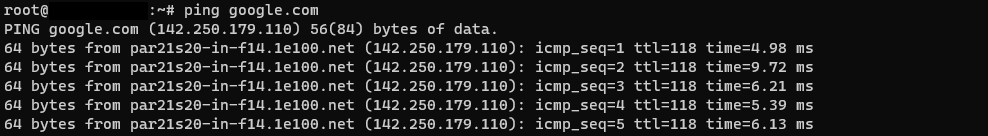
ping google.com
This will give us the following overview:
Windows
On Windows, it will be necessary to open the Windows command terminal and launch the command. Concerning the command prompt, it is possible to open it by doing :
- Type Win + R, a window will open to execute the requested program, it will be necessary to indicate cmd.exe to obtain the terminal. - It is also possible to search for Command prompt in the Start menu.
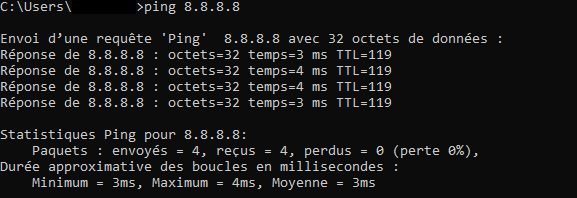
ping 8.8.8.8
This will give us the following overview:
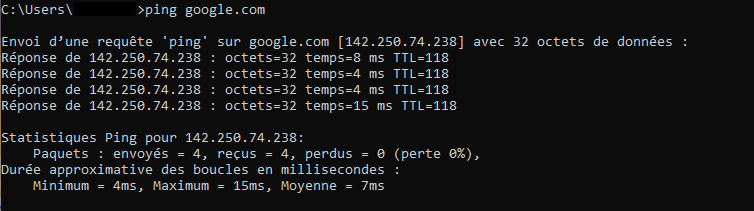
ping google.com
This will give us the following overview:
Mac OS
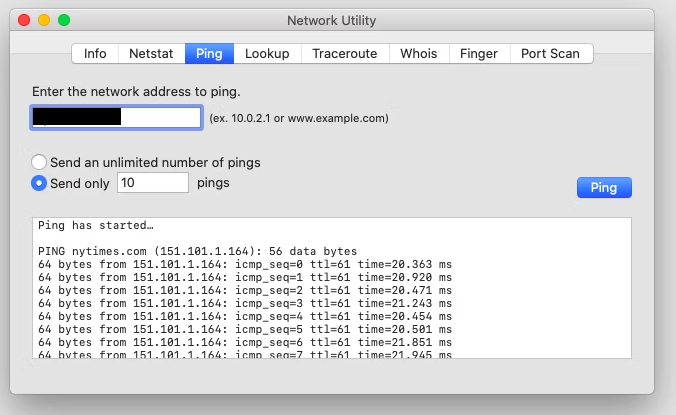
On Mac OS you will need to use the Network Utility application and launch the Ping tool:
- Go to Finder, and launch the search by clicking on the magnifying glass at the top right.
- Type Network Utility and open it.
It is also possible to find it by this path: /System/Library/CoreServices/Applications
Alternatively, for earlier versions of Mac OS it is possible to find the utility here: Finder > Applications > Utilities
- Go to the Ping option, and fill in the field with the domain to test or the IP address.
- Click on Ping.
This will give us the following overview:
Traceroute
A traceroute, or tracert, is a command to follow the route of an IP packet from your local machine to the desired machine or domain.
Linux
On Linux, you will have to open the terminal and install the traceroute command if it is not already the case:
apt install traceroute
Once this is installed, you can run the following command by replacing the IP or domain with the desired one:
traceroute 8.8.8.8
Windows
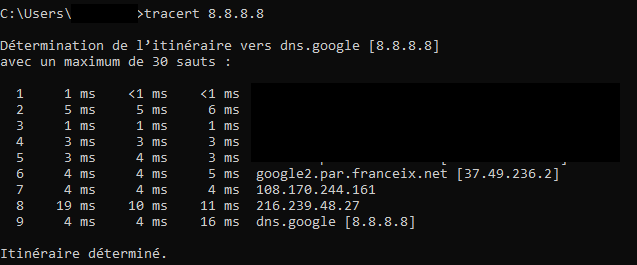
On Windows, it will be necessary to open the Windows command terminal and launch the tracert command as before.
tracert 8.8.8.8
This will give us the following overview:
Mac OS
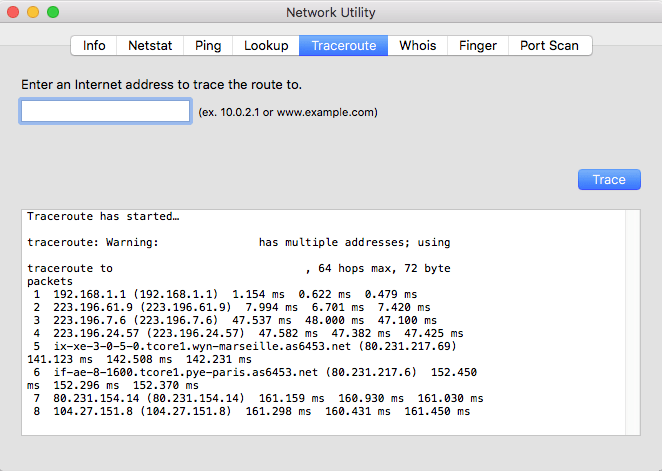
On Mac OS you will still need to use the Network Utility application and run the Traceroute tool:
- Go to the Traceroute option, and fill in the field with the domain to test or the IP address.
- Click on Trace.
This will give us the following overview:
Network configuration
We are going to see different tools allowing us to have all the network information of the local machine.
Linux
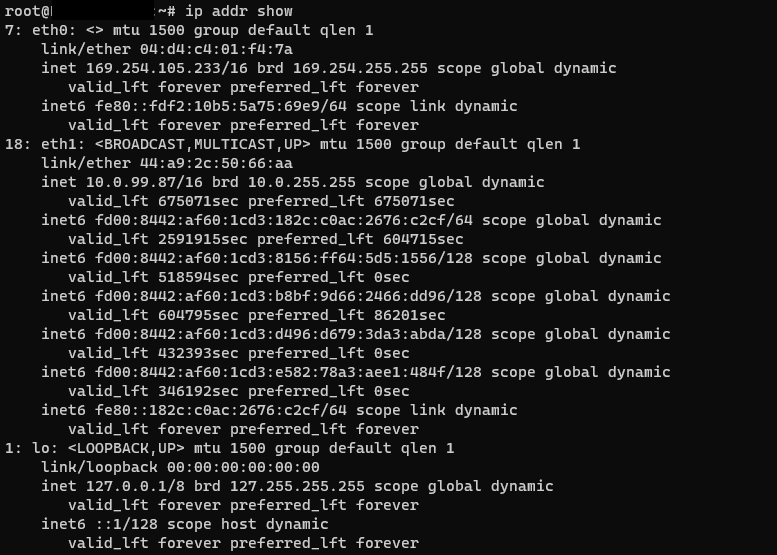
On Linux it is possible to obtain this information with the command ip through the terminal:
ip addr show
This will give us the following overview:
Windows
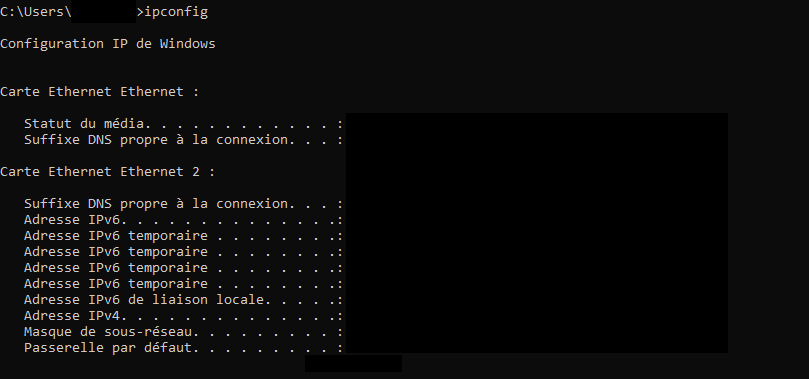
On Windows, you will have to open the Windows command terminal and run the ipconfig command as before.
ipconfig
This will give us the following overview:
Mac OS
On Mac OS it is possible to see this information directly through its interface.
To do this, choose the Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network.
For more information on managing your network on the Mac, here is a guide from Apple support : https://support.apple.com/guide/mac-help/change-network-settings-on-mac-mchlp1102/mac