Restore a Kimsufi server on an Ikoula One VPS Cloud
Restore a Kimsufi server on an Ikoula One VPS Cloud
We are going to make a backup of a Kimsufi server [1] and carry out the restoration on a VPS CIO.
What is the VPS Coud Ikoula One
The Ikoula One Cloud [1] is a turnkey solution that includes an orchestration tool, a load balancer, firewall rules and an EC2 compatible API.
The advantages of the Ikoula One Cloud
- Maitrise des coûts : Une facturation établie à l'avance
- Une infrastructure dédiée: Déploiement d'instances privées
- Garantie de faible latence
- Un outil d'orchestration
- Outil d'orchestration
- Infogérance[2]
Kimsufi server preparation
- Démarrer notre Machine virtuel sur un liveCD, par exemple DebianLive :
- Définir un hostname pour facilement identifier la destination de la restoration
root@debian:~# hostname testrestore
- Installation of Acronis Agent Installation_agent_Linux[[3]]
- Creation of partitions manually
- In case you don't want to have as much disk space
root@debian:~# fdisk /dev/xvda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.33.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): n
Partition number (1-128, default 1):
First sector (34-209715166, default 2048): 40
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (40-209715166, default 209715166): 2048
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux filesystem' and of size 1004.5 KiB.
Command (m for help): n
Partition number (2-128, default 2):
First sector (2049-209715166, default 4096):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (4096-209715166, default 209715166): +97G
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux filesystem' and of size 97 GiB.
Command (m for help): n
Partition number (3-128, default 3):
First sector (203427840-209715166, default 203427840):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (203427840-209715166, default 209715166):
Created a new partition 3 of type 'Linux filesystem' and of size 3 GiB.
Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-3, default 3): 1
Partition type (type L to list all types): 4
Changed type of partition 'Linux filesystem' to 'BIOS boot'.
Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-3, default 3):
Partition type (type L to list all types): 19
Changed type of partition 'Linux filesystem' to 'Linux swap'.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
root@debian:~#
- If you have a backup
Backup:
sfdisk -d /dev/sda > partition.bak
Restoration :
sfdisk /dev/xvda < partition.bak
- Formatting partitions
root@debian:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvda2
mke2fs 1.44.5 (15-Dec-2018)
Creating filesystem with 25427968 4k blocks and 6356992 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 675556c0-d8a0-4c4e-b1fd-87d2b3a0f19e
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (131072 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
root@debian:~# mkswap /dev/xvda3
mkswap: /dev/xvda3: warning: wiping old swap signature.
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 3 GiB (3219103744 bytes)
no label, UUID=315aee13-ed19-4408-8d20-74253a3edbff
root@debian:~#
- Assembly of the partitions or of the partition in our case
root@debian:~# mount /dev/xvda1 /mnt
Restoration
From Acronis interface, we will restore
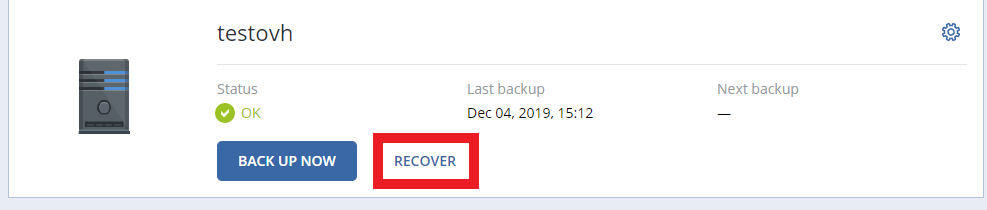
- Select the server to restore and click on 'Recover'
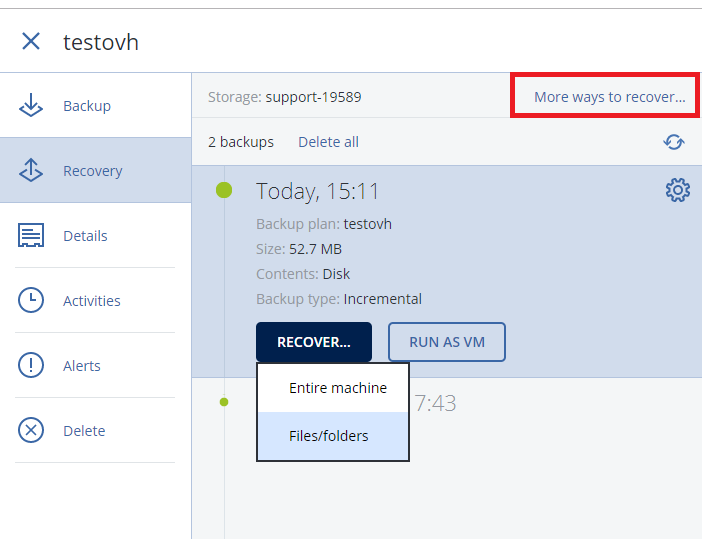
- Click on 'More ways to recover ...' to choose the destination of the restoration.
- Click on 'Recover ...' 'and then on' Files / folders'
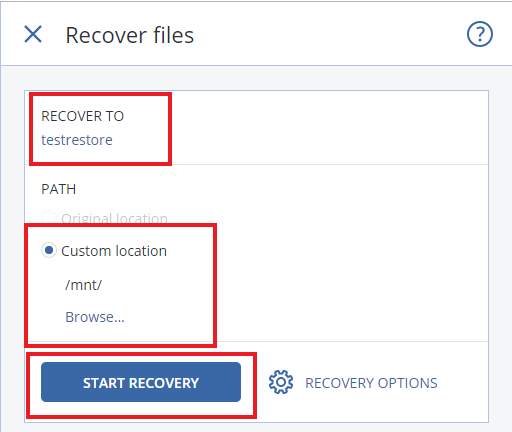
- Navigate the interface to choose all the files and folders included in a partition
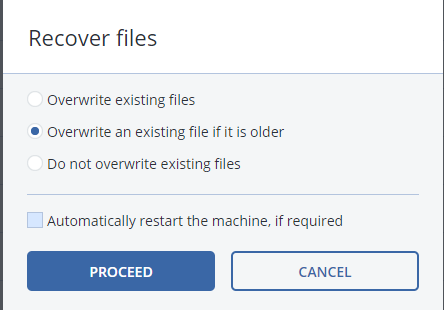
- Confirm the destination, choose the mounting of the partition restore
- Do not select the reboot of the destination because we have not finished
Grub restoration
For this we will use the grub-install method in a chroot.
- We will mount the environment necessary to perform the grub-install in a chroot
mount --bind /dev/ /mnt/dev mount -t proc /proc /mnt/proc mount -t sysfs /sys /mnt/sys
- We are now starting the chroot and launching an update-grud
root@debian:~# chroot /mnt/
root@testrestore:/# grub-install Installation for the platform i386-pc. grub-install : error: the installation device is not specified. root@testrestore:/# grub-install /dev/xvda Installation for the platform i386-pc. Installation complete, error free. root@testrestore:/#
- Modify the file '/ etc / fstab' to take into account
root@testrestore:/# cat /etc/fstab UUID="675556c0-d8a0-4c4e-b1fd-87d2b3a0f19e" / ext4 defaults 0 0 UUID="2ca7f39a-6609-884a-ac1e-8456b66ca755" swap swap defaults 0 0 root@testrestore:/# blkid /dev/xvda2: UUID="675556c0-d8a0-4c4e-b1fd-87d2b3a0f19e" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="ba22cf4d-5988-254b-9f28-d58bc50f7a4f" /dev/xvda3: UUID="315aee13-ed19-4408-8d20-74253a3edbff" TYPE="swap" PARTUUID="2ca7f39a-6609-884a-ac1e-8456b66ca755" /dev/sr0: UUID="2019-11-16-10-15-29-00" LABEL="d-live 10.2.0 st amd64" TYPE="iso9660" PTUUID="1bf56f01" PTTYPE="dos" /dev/loop0: TYPE="squashfs" /dev/xvda1: PARTUUID="f40c93d3-7954-784b-afbb-608d428571fc" root@testrestore:/#
Go further
To improve server compatibility [4] with the CIO and XenServer cloud environment, we will be able to install cloud-init and XenTools: Installation_des_XenTools_sur_une_instance_CloudStack
Adapt configuration
- This migration will involve a change of IP address, you will have to adapt the service configuration files (apache, MariaDB, bind, ...) so that they listen with the IP addresses of CIO.
- In case you use a plesk, [5] here is a KB which will allow you to carry out this modification more simply. How to change the IP address used by plesk