Difference between revisions of "Performance test via a netboot"
(Created page with "<span data-link_translate_fr_title="Test de performance via un netboot" data-link_translate_fr_url="Test de performance via un netboot"></span>:fr:Test de performance via u...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
=== Launching the Netboot === | === Launching the Netboot === | ||
| − | To start your dedicated server in this mode, <b><i style="color:#FF7828"> | + | To start your dedicated server in this mode, <b><i style="color:#FF7828">you need to log in to your [https://extranet.ikoula.com/ Extranet]</i></b> </br> |
| − | Go to <b><i style="color:#FF7828">" | + | Go to <b><i style="color:#FF7828">"Physical server" </i> </b> and choose the server you are interested in.</br> |
Then in the list of features go to <b><i style="color:#FF7828">Netboot</i></b>. | Then in the list of features go to <b><i style="color:#FF7828">Netboot</i></b>. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Netboot_launch.png]] |
| − | <span style="color:#1e195a"> ''' /!\ | + | <span style="color:#1e195a"> ''' /!\ As a reminder, the connection information to the server in Netboot are the identifiers received when your server was delivered /!\ ''' </span> |
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
The command '''fdisk -l''' command allows you to consult the partitions present, their types, their locations and their sizes. | The command '''fdisk -l''' command allows you to consult the partitions present, their types, their locations and their sizes. | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File: Disk_lvm.PNG | 500px ]] |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
If you have encountered any difficulties in following this article, or if you would like to provide any information about it, our technical support team is at your disposal: | If you have encountered any difficulties in following this article, or if you would like to provide any information about it, our technical support team is at your disposal: | ||
<b> | <b> | ||
| − | * 24h/24 et 7j/7 | + | * 24h/24 et 7j/7 by ticket from your Customer Area |
| − | * | + | * Monday to Friday from 9am to 7pm on 01 84 01 02 50 |
</b> | </b> | ||
[[Category:netboot]] | [[Category:netboot]] | ||
[[Category:Dedicated server]] | [[Category:Dedicated server]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:41, 13 March 2023
fr:Test de performance via un netboot
This article has been created by an automatic translation software. You can view the article source here.


When using your dedicated serveryou may need to boot your server on a backup system called Netboot .
Netboot, commonly known as SystemRescue, is an open source operating system, designed to be used without installation to allow administration, restoration or repair of an already installed system on a desktop, laptop or computer server.
Among other things, it allows operations to be performed on a system that no longer boots in normal mode. It completely isolates the equipment from the existing configuration.
In this article, you will find useful commands to test your hardware.
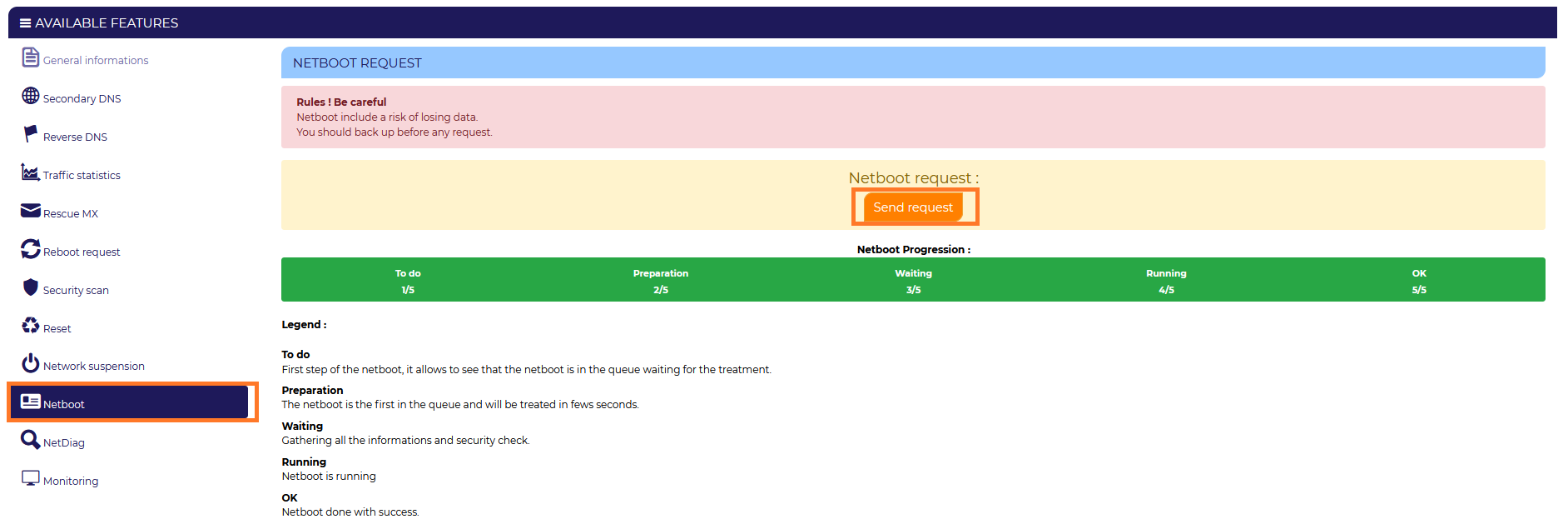
Launching the Netboot
To start your dedicated server in this mode, you need to log in to your Extranet
Go to "Physical server" and choose the server you are interested in.
Then in the list of features go to Netboot.
/!\ As a reminder, the connection information to the server in Netboot are the identifiers received when your server was delivered /!\
Check the temperature
The command sensors command allows you to display the processor's temperatures.
During the various performance tests, it may be useful to run the
watch sensors
This command will continuously monitor the machine's processor temperatures.
Check the integrity of the processor
The command stress command will stress the processor. Thus, the command
stress --cpu 8 --io 4 --vm 2 --vm-bytes 128M --timeout 60m
command will work the processor and memory and test your I/O for 60 minutes.
This is the --timeout option that will set the stress time.
If the test stops unexpectedly in full operation, the processor is no longer able to bear the load and/or is getting too hot.
Check the health of the hard disk
Before performing this test, the structure of the disks must be known.
The command fdisk -l command allows you to consult the partitions present, their types, their locations and their sizes.
Check the health of SATA drives
The command smartctl command allows you to perform a complete test of your hard disk. The following command:
smartctl -d ata -a -f old /dev/<disque>
allows you to have all the useful information about your disk and its current state.
To test your hard disk, run the command:
smartctl -t short /dev/<disque>
Replace short with long for a longer and more complete test.
/!\ Replace /dev/<disque> with the name of your disk (/dev/sda, /dev/sdb, etc...) /!\
Check the health of the NVME disk
Always with the command smartctlcommand, the following command:
smartctl -a /dev/nvme0n1
will also give you all the information you need about your NVME and its current status.
At the end of the test, you will receive a detailed report of the test.
Check RAM memory
This is the memtester command, which will test the integrity of your memory. It is preferable to test the entire memory capacity of your machine.
To do this, type the command:
memtester 16g 2
where you replace 16g with the amount of memory you have (g for giga) and the 2 indicates the number of times the test should be performed.
If you have encountered any difficulties in following this article, or if you would like to provide any information about it, our technical support team is at your disposal:
- 24h/24 et 7j/7 by ticket from your Customer Area
- Monday to Friday from 9am to 7pm on 01 84 01 02 50